How AI can transform lesson planning and assessment
eSchool News
AUGUST 12, 2024
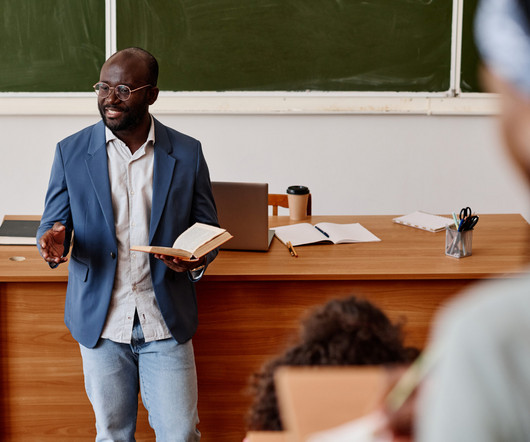
Between budgetary constraints, bandwidth crunches, and a constantly changing syllabus, teachers have their hands full when it comes to structuring and building their class’s lessons and lectures. By distilling a lecture’s knowledge into a set of handy flashcards, teachers can ensure their students’ progress and performance.












































Let's personalize your content